Social Housing Investment – Ultimate FAQ
Social housing investment in the UK offers a unique opportunity for investors seeking stable returns with the added benefit of contributing to social welfare. Backed by government initiatives, these investments provide secure income streams, high yields, and the potential for long-term growth. This comprehensive FAQ addresses key questions investors may have about social housing investment, supported by research data, case studies, and statistical insights.
Introduction
Imagine a world where every family has a safe, affordable place to call home. This vision is becoming a reality through social housing investments in the UK, offering not only stable financial returns but also the satisfaction of contributing to social welfare.
What is Social Housing Investment?
Social housing investment involves purchasing properties that are leased to housing associations or local councils, providing affordable housing for low-income or vulnerable populations. These investments are typically backed by government guarantees, ensuring stable and secure returns.
Social housing investments are structured to meet the housing needs of disadvantaged groups. The government often supports these investments through subsidies and guarantees, making them a low-risk option for investors. The properties are managed by housing associations or local councils, which handle tenant management, maintenance, and repairs, reducing the burden on investors. While social housing investments offer numerous benefits, they also face challenges such as limited grant funding, financial pressures from inflation, and regulatory requirements.
Why Invest in Social Housing?
Investing in social housing offers secure income streams, high yields, and positive social impact. Government backing provides additional security, making these investments a stable and attractive option.
Social housing investments typically yield returns between 9% and 13%, with long-term leases of 5 to 25 years ensuring consistent income. The backing by government schemes like the Affordable Homes Guarantee Scheme reduces the risk of rent defaults. Additionally, these investments contribute to addressing the housing shortage by providing affordable housing to vulnerable populations, enhancing their social impact.
How to Invest in Social Housing?
Investors can invest in social housing through various routes, including purchasing shares in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) focused on social housing, direct property investments, or participating in government-backed loan schemes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Investing in Social Housing:
- Research and Select Investment Options: Determine whether to invest in REITs, direct property purchases, or government schemes. Research each option’s benefits, risks, and potential returns.
- Evaluate Financial and Legal Requirements: Assess your financial capacity and understand the legal requirements involved in purchasing and managing social housing properties, including affordable rent and service charges.
- Understand the Application and Purchase Process: For REITs, this involves purchasing shares through a brokerage. For direct investments, it involves buying property and entering into agreements with housing associations. For government schemes, it involves applying for loans or grants.
- Find Reputable Housing Associations or Investment Platforms: Partner with well-established housing associations or investment platforms that have a track record of successful social housing projects.
Examples of Investment Routes:
- REITs: Investing in REITs like Civitas Social Housing or Home REIT allows investors to buy shares in a portfolio of social housing properties. These trusts manage the properties and handle tenant relations, providing investors with a hands-off investment experience.
- Direct Property Investments: Investors can purchase individual properties designated for social housing. These properties are often leased to housing associations or local councils, ensuring stable rental income.
- Government Schemes: Participating in schemes like the Affordable Homes Guarantee Scheme offers investors the opportunity to provide low-cost loans to housing providers, facilitating the development of new social housing units.
What are the Financial Returns from Social Housing Investments?
Social housing investments typically offer yields ranging from 9% to 13%, with long-term leases providing stable and predictable income.
The financial performance of social housing investments is underpinned by government-funded rental agreements, ensuring high rent collection rates and low vacancy levels. For example, Civitas Social Housing REIT reported an annual rent roll increase of 5% year-on-year, reflecting strong financial performance. These investments also offer inflation-linked returns, providing a hedge against inflation and enhancing long-term financial stability.
What are the Government Initiatives Supporting Social Housing?
Key government initiatives supporting social housing include the Affordable Homes Programme and the Affordable Homes Guarantee Scheme, which provide funding and low-cost loans to housing providers.
- Affordable Homes Programme 2021-2026: This programme aims to deliver 157,000 new homes, including 33,550 for social rent. It provides significant funding to housing associations and local councils to build and upgrade affordable housing units.
- Affordable Homes Guarantee Scheme: This scheme has been expanded in 2024 to offer a total of £6 billion in low-cost loans to housing providers. This supports both the construction of new affordable homes and the upgrade of existing properties, ensuring they meet safety and energy efficiency standards. This scheme helps providers access the necessary funding to expand their business and improve housing quality (GOV.UK) (Barclays Corporate).
What are the Challenges and Prospects of Social Housing Investment?
While social housing investments offer numerous benefits, they also face challenges such as limited grant funding, financial pressures from inflation, and regulatory requirements. However, ongoing government support and new funding mechanisms provide a positive outlook for the sector.
Social housing providers often struggle with financial capacity, particularly in meeting decarbonisation requirements and improving existing council housing standards. Maintenance and repair costs are expected to rise significantly, placing additional financial pressure on housing providers. However, government initiatives and increased institutional investment are helping to mitigate these challenges. The sector is expected to grow, driven by strong demand for affordable housing and continued government support (CBRE).
How do Social Housing Investments Benefit Society?
Social housing investments provide affordable housing to vulnerable populations, addressing the housing crisis and generating a positive impact.
Investing in social housing helps to alleviate the shortage of affordable homes in the UK, providing stable and safe housing for low-income families, the elderly, and individuals with special needs. This not only improves the quality of life for social housing tenants but also contributes to social stability and community development.
Comparison with Other Investments
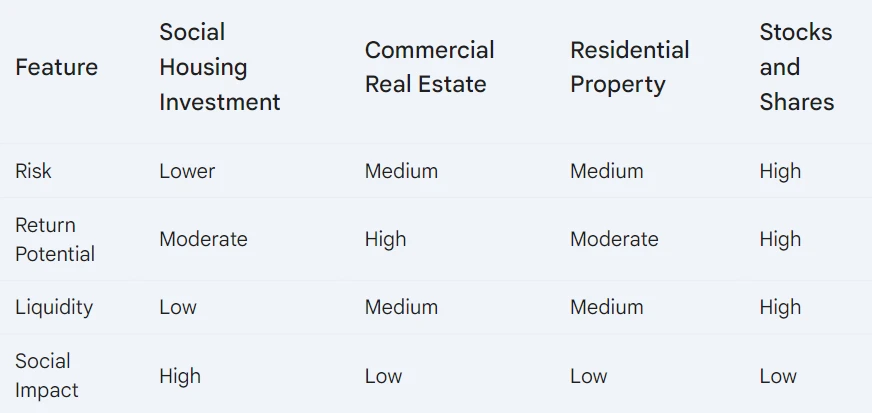
Social Housing Investment Yields: Social housing in the UK typically offers yields in the range of 9% to 13%. These returns are bolstered by government backing and long-term leases, providing stable and predictable income streams. The sector benefits from high rent collection rates and low vacancy levels due to the demand for affordable housing and government support.
Commercial Real Estate Yields: Commercial real estate yields can vary widely depending on the property type and location. For instance, multifamily and neighbourhood retail properties are performing relatively well, offering steady returns. However, sectors like office space are facing high vacancy rates and uncertain futures due to shifts in work patterns post-pandemic. Typical yields for commercial real estate can range from 5% to 7%, with industrial properties showing moderate growth and some signs of softening.
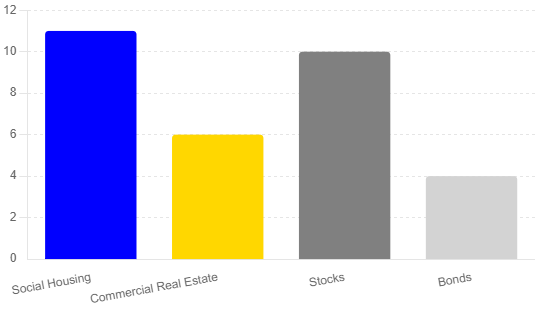
Stock Market Returns: Investing in stocks has historically provided high returns, with long-term averages around 10%. Stocks are highly liquid and offer the potential for significant capital appreciation. However, they come with higher volatility and risk compared to real estate investments.
Bond Yields: Bonds are considered low-risk investments, offering fixed and predictable returns. Government bonds typically yield around 2% to 5%, depending on the current interest rates and economic conditions. While safer, bonds generally provide lower returns compared to stocks and real estate.
Based on this information, social housing investments offer competitive yields compared to other investment types, especially considering their lower risk due to government backing. Here is a summary of typical yields:
- Social Housing: 9% – 13%
- Commercial Real Estate: 5% – 7%
- Stocks: ~10%
- Bonds: 2% – 5%
This comparison highlights that social housing investments are an attractive option for investors seeking stable, high yields with lower risk, particularly in the current economic climate where other real estate sectors face greater uncertainty.
Additional Benefits of Investing in Social Housing:
- Positive Social Impact: Investing in social housing helps to address the housing shortage by providing affordable and secure homes for vulnerable groups, contributing to social stability and community development.
- Diversification: Social housing investments offer diversification benefits compared to traditional investment options. They are less correlated with other asset classes, reducing overall portfolio risk.
- Tax Advantages: Depending on the specific investment structure, investors may be eligible for tax benefits such as tax relief on capital gains or income tax deductions.
- Long-Term Investment: Social housing investments are designed for the long term, offering stable income streams and potential capital appreciation over time.
- Ethical Investment: For investors seeking investments aligned with their values, social housing provides an opportunity to make a positive difference in society while generating financial returns.
By considering these additional benefits, investors can further appreciate the value proposition of social housing investments and make informed decisions about their investment portfolios.
Investing in Social Housing: A Deeper Dive
While the preceding sections have outlined the core benefits and mechanics of social housing investment, it’s essential to consider additional factors and nuances to make informed decisions.
Risk Mitigation and Due Diligence
- Government Support: While government backing is a significant advantage, it’s crucial to understand the specific terms and conditions of government schemes. Changes in government policies or economic conditions may impact the investment landscape.
- Creditworthiness of Housing Associations: Not all housing associations are created equal. Thoroughly assess the financial health and track record of the housing association managing the property.
- Geographical Diversification: Spreading investments across different geographical regions can mitigate risks associated with local economic downturns or changes in housing market conditions.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
- Inflationary Pressures: While social housing rents often have inflation-linked increases, it’s essential to monitor inflationary trends and their impact on overall investment returns.
- Regulatory Changes: The social housing sector is subject to regulatory changes. Staying informed about new regulations and their potential impact on investments is crucial.
- Exit Strategies: Understanding exit strategies is essential. While long-term investments are common in social housing, having a clear plan for potential liquidity needs is important.
The Road Ahead for Social Housing Investment
The social housing sector is poised for continued growth, driven by factors such as increasing population, urbanisation, and the persistent shortage of affordable housing. However, challenges like rising construction costs and the need for sustainable housing solutions require careful consideration.
Investors looking to capitalise on the social housing market should focus on:
- Identifying Emerging Trends: Pay attention to trends like modular housing, sustainable construction, and technological advancements in the sector.
- Building Strong Partnerships: Collaborating with experienced housing associations and developers can enhance investment opportunities.
- Considering Impact Investing: Social housing aligns with impact investing principles, offering opportunities for investors seeking both financial returns and positive social impact.
By carefully assessing these factors and staying informed about industry developments, investors can make well-informed decisions and maximise the potential returns of social housing investments (NatWest Group).
The Broader Impact of Social Housing
Beyond the financial returns for investors, social housing plays a pivotal role in addressing broader societal challenges. By providing stable and affordable housing, social housing contributes to:
- Reducing Homelessness: A significant proportion of the homeless population can be accommodated through social housing, reducing the strain on public services and improving the lives of vulnerable individuals.
- Improving Health and Well-being: Access to safe and affordable housing is linked to better physical and mental health outcomes. Social housing can contribute to healthier communities.
- Supporting Education and Employment: Stable housing provides a foundation for children’s education and enables adults to participate fully in the workforce.
- Strengthening Communities: Social housing can foster a sense of belonging and community cohesion, leading to stronger and more resilient neighbourhoods.
As the demand for affordable housing continues to grow, the social housing sector is likely to attract increasing attention from investors, policymakers, and the public. By understanding the complex interplay of social, economic, and environmental factors, investors can position themselves to capitalise on the opportunities while contributing to a more equitable and sustainable society.
Key Takeaways
- Stable Returns and High Yields: Social housing investments typically offer yields between 9% and 13%, with long-term leases providing consistent income streams. Government backing further enhances the stability and attractiveness of these investments.
- Positive Social Impact: Investing in social housing helps address the housing shortage, providing secure and affordable homes for vulnerable groups, and contributing to social stability and community development.
- Government Support: Key initiatives like the Affordable Homes Guarantee Scheme and the Affordable Homes Programme provide significant funding and low-cost loans to housing providers, supporting both new construction and upgrades to existing properties.
- Challenges and Prospects: Despite challenges such as rising maintenance costs and regulatory pressures, the sector benefits from strong demand and ongoing government support. Strategic investments and partnerships can help mitigate these challenges.
- Comparative Advantage: Compared to other investment types, social housing offers competitive yields with lower risk, making it an attractive option for investors seeking both financial and ethical returns.
By understanding these key aspects, investors can make informed decisions and leverage the potential of social housing investments.